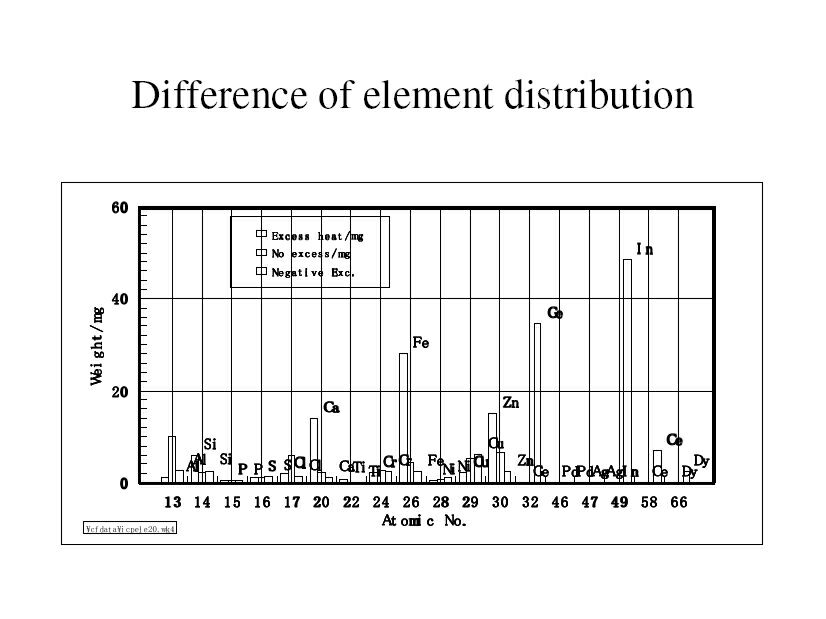

| We have analyzed the element existing in the electrode and the electrolytes by EDX and XPS method for estimate the entire element in the electrolysis system. After that difference of the element deposition for these three cases were changed as indicated as in figure. |
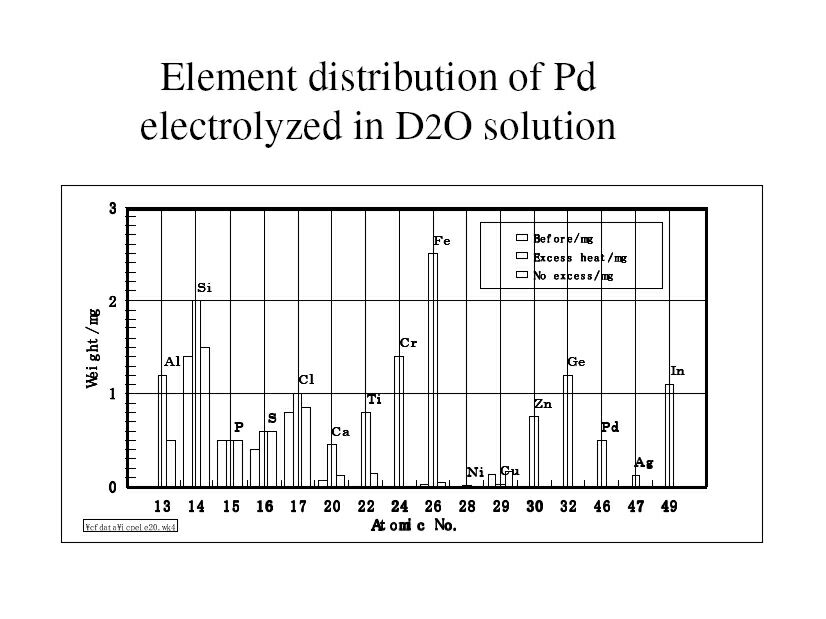
| In the case of total elements deposition of excess heat generated electrolyte and electrode; the distribution of the elements is similar with the result of Palladium electrode that showed many elements deposition after excess heat generated by electrolysis in heavy water electrolysis as shown in figure. Conversely, in the case of endothermic heat is completely different; in particular, heavy element deposition can be observed in the spectrum. |
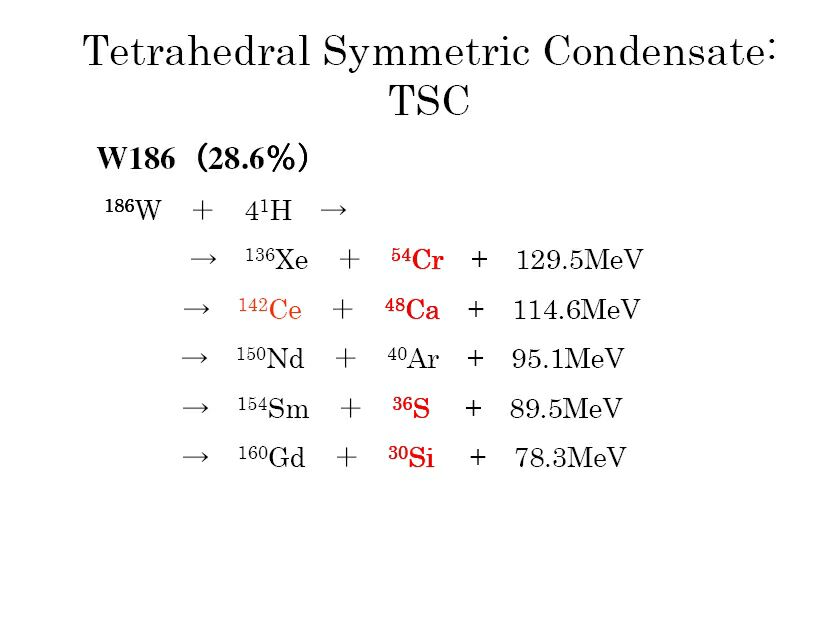
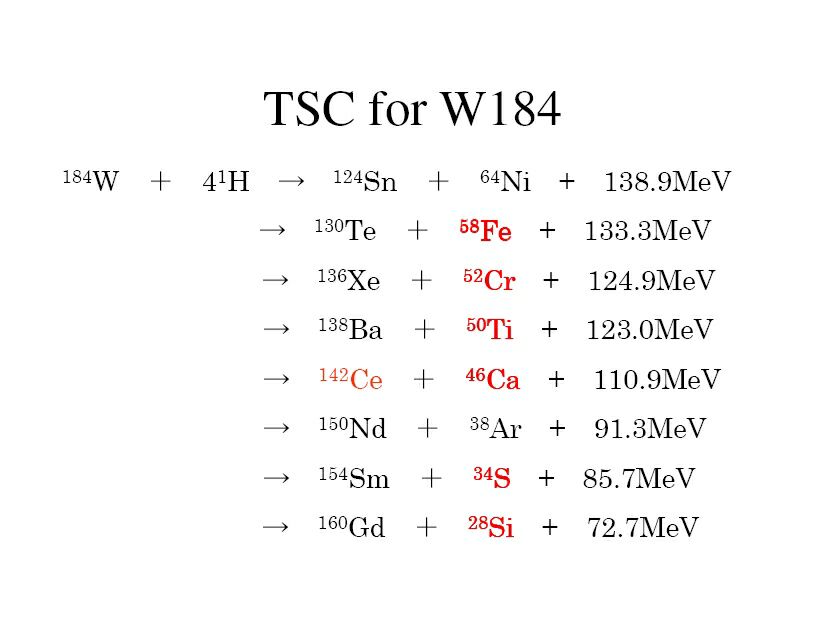
| It is still difficult to find out exact relationship between the current efficiency, e and other factors. However, we can strongly suggest that one of the key factors seems the input voltage that shows in figure of the e and V relationship. Here, it can be understand that the e has a tendency of increase with input voltage. One point of e value in the figure shows up to twice of the theoretical value of unity; the point was obtained by the result of plasma electrolysis. On the other hand, the e is remaining at unity for all of the other normal electrolysis. It can be expected that if the input Voltage were increased toward several hundred V, then the e would exceed far than the value of unity. |
![]() Download the full Pdf document (
1.12 Mb)
Download the full Pdf document (
1.12 Mb)
PATENTS
from MIZUNO TADAHIKO (JP) :
Abstract
: PROBLEM
TO BE SOLVED: To provide a method for generating a
hydrogen gas with a high efficiency by continuously and
directly pyrolyzing water with a satisfactory
controllability.
Abstract
: A
thermal energy extraction apparatus comprises an
electrolyte bath (1), electrolytic solution (4),
electrodes (2, 3), an atomic nuclear fission means (11),
and a thermal energy extraction means (5, 6a, 6b,
13a-13e, 14, 23a, 23b). The electrolytic solution (4) is
kept inside the electrolyte bath (1) and contains at
least light water or heavy water. The electrodes (2, 3)
are so arranged as to be in contact with the electrolytic
solution (4) and include an anode (3) and a cathode (3).
The atomic nuclear fission means (11) fissions atomic
nuclei of the material constituting the electrodes (2, 3)
by applying a voltage and a current to the electrodes (2,
3). The thermal energy extraction means (5, 6a, 6b,
13a-13e, 14, 23a, 23b) extracts heat medium (18, 19, 21,
22a, 22b) heated by the thermal energy generated by the
fission of the atomic nuclei of the material constituting
the electrodes (2, 3) to the outside of the electrolyte
bath (1).
Abstract
: A
reactor for producing energy and neutrons by electrolytic
reaction in a light- or heavy-water solution comprises a
base made of a refractory metal and a metal layer formed
on the base and active against hydrogen. The reactor to
serve as a cathode is immersed in an electrolyte together
with an anode. Current is made to flow between the
cathode and anode to cause an electrolytic reaction.
Thus, thermal energy and neutrons are produced.
|

Note from Jean-Louis Naudin : I am very grateful to Tadahiko Mizuno et Al. for the sharing of their excellent work about this fascinating field of research.